We offer medical detox and multiple addiction treatment options in our
luxury treatment centres in Port Hope, Cobourg, and Ottawa.
How Addictive is Meth for the Brain?
Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, is one of the most addictive drugs, causing devastating effects on both the brain and the body. Its chemical composition and interaction with the brain reveal the severity of meth addiction and underscore the importance of seeking treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Methamphetamine's High Addictiveness: Methamphetamine, or meth, is an extremely addictive stimulant that significantly impacts the brain's reward system, making it one of the hardest substances to quit.
- Brain Damage: Meth increases dopamine levels, causing euphoria but leading to long-term brain damage.
- Symptoms of Addiction: Physical signs of meth addiction include severe weight loss, dental decay (“meth mouth”), and skin sores, while behavioural and psychological symptoms encompass erratic behaviour, paranoia, and violent tendencies.
- Recovery is Possible: With proper care and support, long-term recovery from meth addiction is achievable.
What Is Methamphetamine?
Methamphetamine, often referred to as meth, is a potent and highly addictive stimulant that affects the central nervous system. It is chemically similar to amphetamine, a drug used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy, but meth is much more potent therefore poses greater dangers.

Chemical Makeup and Forms
Methamphetamine's chemical structure includes an additional methyl group, which allows it to more effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier. This can lead to a more profound and longer-lasting effect on the brain. Generally, meth typically appears as a white, odourless, bitter crystalline powder that can be taken orally, snorting, injected or smoked. The latter two methods deliver the drug to the brain and bloodstream faster, creating an intense “rush.”
Common Uses and Immediate Effects
While methamphetamine has some limited medical uses — such as treating ADHD under the brand name Desoxyn — its widespread use is largely due to its extremely powerful effects when used non-medically. Meth produces an intense euphoria, heightened alertness, and a surge of energy. However, these short-term benefits as a recreational drug come with meth highly risks.
Meth raises dopamine levels in the brain dramatically. Dopamine is involved in body movement, motivation, and reinforcing rewarding behaviours. Methamphetamine causes a surge in dopamine that reinforces drug-taking behaviour, making meth very addictive.
Health Risks and Addiction Potential
Meth is highly addictive because of its powerful effects on the brain’s reward system. Even with short-term use, meth can lead to a cycle of binging and crashing, as users chase the drug’s potent euphoric effects. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on meth to release dopamine, making it difficult to experience the same pleasure from other activities. Other adverse health effects of meth include cardiovascular problems, hyperthermia and irreversible damage to blood vessels in the brain, which can lead to strokes.
Effects of Meth on the Brain
Understanding how addictive meth is requires a closer look at its effects on the brain. Meth dramatically alters brain chemistry, leading to both short-term euphoria and long-term cognitive and emotional damage.
Dopamine Release and Addiction Development
Meth’s impact on the brain primarily stems from its ability to massively increase dopamine release, a neurotransmitter central to the brain's reward and pleasure centres. This flood of dopamine creates the intense high associated with meth use and lays the foundation for addiction. As the brain becomes dependent on this dopamine surge to function normally, dependency develops — a key factor in meth’s high addiction potential.

Short-Term Effects on the Brain
In the short term, meth increases alertness, energy, and euphoria. However, these effects come at a steep price. Meth use can lead to confusion, irritability, anxiety, and increased aggression. The intense high is often followed by a "crash" characterized by extreme fatigue, depression, and anxiety. Even after just a few uses, these effects demonstrate meth’s powerful grip on the brain.
Long-Term Mental and Emotional Damage
Long-term meth use leads to severe brain damage, including significant cognitive decline, memory loss, and learning deficiencies. Chronic users often experience severe emotional distress, including paranoia, hallucinations, and violent behaviour. These issues result from the destruction of dopamine receptors in the brain, which sometimes becomes irreversible, making it difficult for users to derive pleasure from anything other than the drug. Over time, methamphetamine causes irreversible damage to both the structure and function of the brain.
Signs & Symptoms of Meth Addiction
Recognizing the signs of meth addiction is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Meth addiction manifests in various physical, behavioural, and psychological symptoms.
Physical Symptoms
The signs of a meth addict can often manifest themselves within the body. The more common physical symptoms of a meth addict are extreme weight loss due to the appetite-suppressing abilities of the drug. Bad dental health, which is known as “meth mouth”, includes tooth decay, advanced gum diseases, and tooth loss. More common ones include skin sores that generally occur because of obsessive picking; they often have a gaunt appearance, which gives them an overall unhealthy look.
Behavioural and Psychological Symptoms
Behaviorally, meth addicts often act erratically and unpredictably. They may withdraw socially, lose interest in activities they once enjoyed, and neglect work or household responsibilities. Common psychological symptoms of meth use include paranoia, hallucinations, and violent behaviour. Anxiety and depression can be severe, especially during withdrawal periods.

Long-Term Consequences
As meth addiction progresses, the signs become more pronounced, with devastating effects on the body and mind. Long-term users often struggle with basic cognitive functions and suffer from severe emotional distress, leading to social isolation, ruined relationships, and a diminished quality of life. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for seeking help before irreparable damage occurs.
Treatment Options for Meth Addiction
Recovery from meth addiction is challenging, but with the right support and treatment, it is possible. A comprehensive approach to meth addiction treatment includes detox, therapy, and long-term support.
Detoxification
Treatment for meth addiction begins with detoxification, a process of eliminating the drug from the body. This process can be physically and emotionally challenging as the body readjusts to functioning without meth. Common withdrawal symptoms include intense cravings, depression, anxiety, and general weakness. Medical professionals often advise that detoxification be conducted under close supervision to help manage withdrawal symptoms and prevent relapse.
Behavioural Therapy and Counseling
Behavioural therapy is the cornerstone of meth addiction treatment. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in helping users recognize and change the thought patterns that lead to drug use. Individual counselling provides a safe space for patients to explore underlying issues that may have contributed to their addiction and to develop coping strategies for the future.
Support Groups and Aftercare
Support groups like Narcotics Anonymous offer long-term support and accountability for those recovering from meth addiction. These groups provide a sense of community and a network of people who understand the challenges of recovery. After completing formal treatment, many individuals benefit from ongoing counselling and aftercare programs to prevent relapse.

Extensive Care for Long-term Recovery
Effective drug rehab programs for meth addiction address every aspect of an individual’s life. Treatment should include medical and psychological interventions, as well as support for adopting a healthy lifestyle, which may involve job training, education, and repairing relationships with family and friends. Long-term recovery is an ongoing process that requires continuous commitment and support.
Breaking the Chains: A Path to Recovery
Meth is an incredibly powerful and dangerous drug, both physically and psychologically. Understanding what methamphetamine is, how it affects the brain, and the signs of addiction can prompt individuals to seek treatment urgently. The recovery process is difficult, but with excellent care and long-term support, individuals can reclaim their lives from addiction and build a healthy, fulfilling future.
FAQ
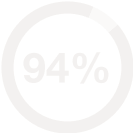
How addictive is meth?
Methamphetamine is a highly addictive substance since it works in the brain to strongly reward. Tremendous amounts of dopamine are released with the drug, creating strong dependency and a hard feeling to let go. This makes meth one of the most difficult substances to give up.
What are the signs that somebody is addicted to meth?
Meth users often show signs of extreme weight loss, dental problems, erratic behaviour, paranoia, and cognitive decline. You may also note some bodily physical signs such as “meth mouth” and sores on the skin body.
What are the long-term effects of using meth?
Long-term effects of meth use include a drastic reduction in cognitive abilities, loss of memory, serious emotional disturbances, and brain damage, which is irreducible. These effects can persist for years even after the individual stops using meth.
What are the modes of treatment available for meth addiction?
Treatment typically includes detoxification, behavioural therapy, and counselling, along with support groups. Comprehensive care and long-term support are key to successful recovery.
Can someone recover from an addiction to meth?
Yes, recovery from meth addiction is possible with the right treatment and support. It involves personal therapy, support groups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle on the way to long-term recovery.