We offer medical detox and multiple addiction treatment options in our
luxury treatment centres in Port Hope, Cobourg, and Ottawa.
The Side Effects of Biphentin and Its Risks
Biphentin stands at the forefront of ADHD treatment options available to Canadian patients, offering methylphenidate in a sophisticated extended-release format. By adjusting key neurotransmitters, this prescription helps calm overactivity and sharpen focus in those struggling with attention difficulties. Health authorities across Canada recognize Biphentin as an appropriate intervention for patients ranging from elementary school children (ages 6 and above) to teenagers and mature adults seeking symptom relief.
Key Takeaways
- Biphentin is an extended-release ADHD medication approved for Canadians aged six and up, improving focus and reducing hyperactivity.
- Common side effects include appetite loss, headaches, sleep issues, heart rate changes, and anxiety, some requiring medical attention.
- Addiction risk is low when used correctly, but rises with misuse or in those witha substance abuse history.
- Long-term use needs monitoring of growth in children, heart health, and mental state, especially in vulnerable patients.
- Regular doctor visits and honest communication help manage side effects and ensure safe, effective treatment.
Though clinical success stories abound with Biphentin therapy, prospective users must weigh the benefits against potential complications before beginning treatment. Our analysis offers insights into reported reactions, addresses questions about possible dependence, considers the implications of ongoing usage, and provides specialized guidance for various patient populations considering this medication.

Common Side Effects of Biphentin
Users typically experience a range of reactions when taking Biphentin, varying from mild discomfort to more serious concerns that might require medical intervention.
Physical Side Effects
The physical responses to Biphentin vary considerably among patients:
- Appetite changes:
- Reduced hunger affects approximately 25% of patients
- May result in gradual weight loss throughout treatment periods
- Headaches:
- Approximately 25% of young patients report headache symptoms
- About 28% of adult users experience headaches
- Sleep disturbances:
- Difficulty initiating sleep impacts roughly 22% of adults
- Between 7-22% of younger patients taking this medication experience disrupted sleep patterns
- Cardiovascular effects:
- Quickened pulse
- Occasional heart rhythm awareness
- Modest blood pressure elevations
- Oral symptoms:
- Dry mouth affects approximately 12% of adult patients taking Biphentin
- Dry mouth affects approximately 12% of adult patients taking Biphentin
- Digestive issues:
- Stomach upset
- Occasional vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort occurs unpredictably across various age categories
Psychological Side Effects
Mental and emotional shifts commonly accompany Biphentin regimens:
Anxiety symptoms:
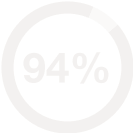
- Heightened uneasiness affects approximately 24% of adult patients
- About 27% of teenage patients experience anxiety
- Anxiety is the most common psychological side effect in patients taking Biphentin
Mood changes:
- Emotional unpredictability
- Unexpected temperament fluctuations
- Increased irritability
- Amplified emotional lability throughout treatment
Restlessness:
- Approximately 6% of adult patients develop noticeable agitation
- Typically manifests during initial adaptation phases
- May continue indefinitely for certain individuals
- Often requires ongoing management approaches and professional supervision
When Medical Help Becomes Necessary
Though numerous side effects of Biphentin diminish with continued use or dosage adjustments, certain symptoms demand prompt professional evaluation. Any chest discomfort or unusual sensations warrant immediate medical consultation, as do respiratory difficulties or unexpected consciousness lapses. Severe, persistent headaches differing from established patterns might signal complications requiring thorough assessment.
Visual disturbances, including difficulties with focusing or other sight irregularities, should never be dismissed when taking this medication. Significant mood deterioration beyond typical fluctuations, particularly involving aggressive impulses or self-harm considerations, requires urgent intervention. The emergence of involuntary movements, verbal repetitions, or pronounced physical restlessness also necessitates medical consultation to evaluate potential adverse medication reactions.

The Addiction Question: Is Biphentin Addictive?
Understanding Addiction Risk
Many patients express concern about potential dependency issues with Biphentin. This methylphenidate-based stimulant carries a Schedule II classification under Canadian regulations, acknowledging legitimate therapeutic applications alongside potential misuse concerns. The core component, methylphenidate, shares certain addictive characteristics with amphetamine compounds, though this risk primarily manifests when usage deviates from prescribed guidelines.
A fundamental distinction separates therapeutic application from misuse: when administered according to medical directives for ADHD management, Biphentin rarely triggers dependency patterns among patients. The controlled-release engineering helps minimize Biphentin's addiction potential compared to immediate-release stimulant variants by delivering gradual, extended effects rather than intense concentration surges that might reinforce problematic consumption habits.
Factors That Increase Dependency Risk
Utilizing methylphenidate beyond medical recommendations can foster tolerance development and psychological reliance over extended periods. Medical professionals should maintain vigilant oversight for patients with substance abuse backgrounds during Biphentin therapy, as established patterns might suggest heightened vulnerability to problematic use. Previous substance dependencies, whether personal or within immediate family circles, create elevated risk profiles for certain patients.
Exceeding prescribed dosages, manipulating administration methods through tablet crushing, unauthorized medication use, or combining Biphentin with alcohol or recreational compounds significantly increases the likelihood of dependency. These behaviours disrupt the medication's intended delivery sequence and may produce intensified effects that encourage problematic usage patterns and potential Biphentin addiction.
Biphentin Classification
There is a common misconception that Biphentin is an opioid. Biphentin differs fundamentally from opioid substances, despite occasional classification confusion. As a stimulant containing methylphenidate hydrochloride, Biphentin influences entirely different neurological systems and generates distinctly different responses than opioids. Though both medication categories carry dependency concerns, they represent completely separate pharmacological classifications with distinct safety profiles and therapeutic applications. The misconception about Biphentin being an opioid represents a common misunderstanding requiring clarification for patients evaluating treatment possibilities.
Long-term Effects and Concerns
Growth Effects in Children
Young patients taking methylphenidate-based treatments like Biphentin may experience developmental changes during extended therapy. Clinical observations indicate an average height reduction of 2 cm and a weight decrease of 2.7 kg following thirty-six months of uninterrupted treatment. Healthcare providers typically implement thorough growth monitoring throughout the therapeutic journey, including regular height and weight documentation at standardized intervals.
Many physicians suggest periodic medication interruptions (medication holidays) during academic vacations or other suitable timeframes to evaluate ongoing treatment necessity and to minimize potential developmental impacts. Treatment modifications frequently follow if significant growth concerns emerge, and potential dosage adjustments or alternative therapeutic approaches are considered to balance symptom management with developmental requirements.

Cardiovascular Considerations
Extended methylphenidate administration requires attentive cardiovascular monitoring due to its stimulant properties. Biphentin may elevate blood pressure and heart rate, potentially creating risks for vulnerable patients with pre-existing conditions. Regular cardiac assessment becomes particularly crucial during long-term treatment protocols.
Individuals with structural heart irregularities, rhythm abnormalities, coronary vessel disease, or similar cardiac conditions generally shouldn't receive stimulant medications due to increased risks of serious cardiovascular events. Though uncommon, cases of sudden death have occurred in patients with underlying cardiac vulnerabilities, emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive screening and continuous monitoring throughout Biphentin treatment.
Mental Health Impacts
Extended Biphentin use might influence mental health functioning for certain individuals, particularly those with pre-existing vulnerabilities. Some children and adolescents without previous psychiatric history have developed psychotic or manic manifestations while taking methylphenidate-based medications. These can include perceptual disturbances, thought pattern anomalies, pronounced aggression, heightened anxiety, or unusual agitation states.
Self-harm considerations occasionally emerge during treatment, particularly when initiating medication or implementing dosage modifications. This risk necessitates vigilant monitoring protocols, especially for patients with pre-existing psychological conditions or family histories of mood disturbances. Regular psychiatric evaluation helps identify emerging concerns before they develop into serious complications or require treatment discontinuation.
Special Populations and Considerations
Different patient groups may experience unique side effects of Biphentin or face specific risks.
Children and Adolescents
Health authorities permit Biphentin use only for youth aged 6 and above, explicitly excluding younger children from treatment eligibility. Growing youngsters need far more intensive growth surveillance than their adult counterparts, with physicians carefully documenting weight changes, height progression, and broader developmental milestones throughout therapy. Young bodies often respond differently to the side effects of Biphentin than fully matured systems do, with many families noticing more dramatic mealtime resistance or bedtime complications in their children.
For youngsters still developing physically, doctors must periodically question whether continued medication remains necessary or whether dosage modifications would better suit their evolving needs. Pediatric specialists typically establish formalized check-in schedules, with particular attention during key growth phases, to verify that the treatment delivers symptom improvement without compromising physical development or causing unnecessary discomfort.
Adults with Pre-existing Conditions
Adults with certain health conditions require special attention:
- Heart conditions: Those with cardiovascular issues, hypertension, or family cardiac history need thorough evaluation before starting Biphentin.
- Psychiatric disorders: Patients with psychosis, bipolar disorder, depression, or suicidal thoughts require careful observation.
- Seizure disorders: Methylphenidate may reduce seizure thresholds in susceptible individuals.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnant women should only take Biphentin when the benefits clearly outweigh the potential fetal risks. No definitive safety studies exist for methylphenidate during pregnancy.
For nursing mothers, methylphenidate appears in breast milk at a milk-to-plasma ratio of approximately 2.5. This creates potential risks for nursing infants, requiring thoughtful consideration of breastfeeding benefits versus treatment needs.

Managing Side Effects and Risks
Working with Healthcare Providers
An effective partnership with medical professionals is essential for managing the side effects of Biphentin:
Communication strategies:
- Document all side effects, even minor ones
- Report symptoms promptly to your doctor
- Discuss any concerns about dependency openly
- Share your complete medication experience
Regular medical follow-up:
- Attend all scheduled evaluations
- Participate in effectiveness assessments
- Be prepared for possible treatment adjustments
- Request additional appointments if new side effects emerge
Providing useful feedback:
- Describe symptom changes specifically
- Explain how side effects impact daily activities
- Share both improvements and challenges
- Discuss quality-of-life concerns honestly

Finding Balance
When used correctly, Biphentin helps many Canadians manage their ADHD symptoms. People often notice they can focus better, control impulses, and handle daily tasks more smoothly. Knowing about the possible side effects of Biphentin lets everyone make better choices about treatment.
Yes, misuse can lead to Biphentin addiction, but for most people who take it properly, the benefits make a real difference. Its slow-release design provides steady support throughout the day without the ups and downs of other medications.
If you're having trouble with side effects, talk to your doctor. Working together to create a plan that fits your specific situation often leads to the best outcomes. Every person responds differently to medication, and finding the right approach might take some adjustment.
FAQ
Is Biphentin addictive when taken as prescribed?
When followed exactly as prescribed for ADHD treatment, Biphentin addiction risk remains minimal due to its controlled-release engineering. However, as a Schedule II controlled substance containing methylphenidate, patients with a history of substance use require attentive clinical monitoring.
What are the most common side effects of Biphentin?
The most frequent side effects of Biphentin include reduced appetite (affecting 20-26% of patients), headaches (troubling 25-28%), sleep disturbances, nervousness, and anxiety. Most reactions appear during early treatment phases and frequently diminish with continued use.
Can Biphentin affect my child's growth?
Yes, Biphentin can influence pediatric development during extended treatment, with research revealing an average decrease of 2 cm in height and 2.7kg in weight in comparison to expected growth, following thirty-six months of therapy. Medical providers monitor growth parameters regularly and may recommend periodic medication interruptions.
Is Biphentin an opioid medication?
No. It is a misconception that Biphentin is an opioid. Biphentin contains methylphenidate hydrochloride, which is categorized as a central nervous system stimulant. Unlike sedative opioids, Biphentin increases alertness and mental activity.
How long do the side effects of Biphentin typically last?
Most side effects of Biphentin emerge during the initial weeks of treatment and diminish as physiological adaptation occurs, typically improving within 2-4 weeks. The medication's therapeutic effects last 10-12 hours per dose, with side effects generally following similar duration patterns.