We offer medical detox and multiple addiction treatment options in our
luxury treatment centres in Port Hope, Cobourg, and Ottawa.
How Addictive is Ketamine? Unveiling the Hidden Dangers
The allure of using ketamine has grown beyond its medical roots to its euphoric and dissociative effects. However, the hidden dangers lurking beneath this substance can quickly turn curiosity into a struggle with ketamine addiction. As more people start experimenting with this powerful drug, it becomes even more vital to understand its addictive nature. This article looks at the complex nature of ketamine's addictive potential, exposing the risks and underlining the urgency of awareness.
Key Takeaways
- Addictive Potential: Ketamine, originally a medical anesthetic, is now often misused for its euphoric effects, raising addiction concerns.
- Medical vs. Recreational Use: While effective in treating severe depression, recreational use of ketamine, especially in clubs, risks severe dependence.
- Health Risks and Legal Status: Misuse can cause bladder and kidney damage, cognitive issues, and mental health disorders. It is a Schedule III controlled substance.
- Signs of Addiction: Increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, compulsive use, neglecting duties, and social isolation are key signs of addiction.
- Treatment Options: Effective treatments include detoxification, behavioural therapies, medication-assisted treatment, and long-term support from groups and aftercare programs.

What Is Ketamine?
Ketamine was developed as a powerful anesthetic for use in medicine, but with time, it has taken up a dark path into the world of recreation. What was first applauded for its safe anesthesia-inducing capabilities is now hunted for its mind-altering effects. This switch raises critical concerns about ketamine’s potential to become addictive, as its use extends beyond controlled medical environments into far more dangerous, unregulated territory.
Medical Uses of Ketamine
Its medical applications go much beyond the original use of this drug as an anesthetic. Of late, it has gained importance for its off-label use in the treatment of severe depression. Given in a medically controlled environment, ketamine works quickly to reduce depressive symptoms and has given hope to many people who were previously nonresponsive to standard therapies. However, the therapeutic potential of this medication is not without an equal level of potential for addiction, which warrants careful monitoring and professional oversight to avoid misuse and addiction.
Recreational Use and Misuse of Ketamine
Ketamine has gained popularity in recreational use as it can provoke massive doses of euphoria and dissociative effects. It has become trendy in club and party circles, known colloquially as "Special K." Users of ketamine can feel a superhuman level of detachment from reality and can have vivid, dream-like states from ketamine. The critical question arises of exactly how addictive is ketamine?
Initially considered an innocent getaway, frequent abuse can lead to severe psychological and physical dependence. Users may find themselves needing more of the drug to get the same effect as tolerance builds, and so it spirals upward with the amount consumed. This might be a decoy for the user, and once addiction takes hold, the hidden dangers of this apparently exciting substance are revealed. Understanding these risks is crucial in addressing the broader implications of ketamine misuse in recreational settings.

Legal Status of Ketamine
Ketamine is a very potent drug that finds its use in medicine; therefore, it needs regulation. It is a Schedule III controlled substance, reflecting its legitimate medical uses and potential for misuse. In this respect, this status underlines the necessity of controlling such administration to avoid ketamine abuse but allows its benefits to be realized in clinical settings. Both these aspects need to be balanced appropriately to reduce the risks associated with this potent substance.
The Addictive Nature of Ketamine
The potential for ketamine addiction is increasingly frightening as its use expands beyond a medical setting. Dependence on ketamine might be acquired very fast, leading to the development of physical and psychological dependence. It is of great importance to understand its effects on the human body and to be able to identify the signs and symptoms of addiction. In the following sections, we will discuss the specifics of how ketamine impacts the human body and how to identify addiction at an early stage.
Physical Dependence and Tolerance
Ketamine's effects on the brain essentially bring about its addictive nature. Repeated use of ketamine results in the phenomenon of tolerance; that is, the brain needs increased doses to achieve the same feelings of euphoria. This can snowball into physical dependence very fast. Medical experts agree that the potential for addiction to ketamine is moderate, but its dissociative effects make it very desirable and habit-forming. As tolerance builds, the user may find himself in a cycle of increased use, which represents an urgent call for awareness and early intervention.

Psychological Dependence
Psychological dependence on ketamine is as challenging to overcome as physical dependence. The ability to produce euphoria and detachment from reality makes this drug a habitual substance of use. Key factors contributing to psychological dependence include:
- Cravings: These are compelling desires to use ketamine, mainly brought on by stress or environmental cues.
- Psychological dependence: Using ketamine to escape the hassles of daily life or emotional hurt.
- Behavioral patterns: Repeated use in spite of negative consequences.
Addressing psychological dependence is crucial in addiction treatment, focusing on breaking these harmful patterns and developing healthier coping mechanisms.
Comparison with Other Addictive Substances
Compared to other addictive drugs, ketamine gives off a very different profile. It is considered generally less physically addictive than opioids or amphetamines, but the psychological addiction potential remains high. The capacity of ketamine to produce great dissociative states can be singularly compelling, particularly for persons with mental health challenges. This aspect makes ketamine uniquely addictive yet just as concerning. Understanding these delicate shades of distinction is vital in addressing the risks that come with its use.
Signs and Symptoms of Ketamine Addiction
Ketamine addiction is identifiable through its characteristic signs and symptoms. Here are some of the key signs of a person becoming addicted to ketamine:
- Increased tolerance: Larger doses are required to achieve the same effects.
- Withdrawal symptoms: exhibited by anxiety, depression, and other cravings when not using ketamine.
- Compulsive use: More frequent and more significant amounts of ketamine than intended.
- Neglecting responsibilities: Failing to meet obligations related to family, job, or school due to use.
- Social withdrawal: Staying away from family and friends, wanting to use ketamine alone.
These signs, when tackled early enough, can really promote successful addiction treatment and recovery. Early recognition and professional assistance are essential in mitigating the long-term impacts of ketamine addiction.

Health Risks Associated with Using Ketamine
Using ketamine out of a medical context has many serious health risks. Though there are proven benefits from the use of ketamine therapy under professional control, many instances of its use outside this context result in serious health issues. Some of the significant health risks of using ketamine include:
- Bladder: Chronic use can result in painful and debilitating conditions.
- Kidneys: Long-term use may seriously damage the functioning of the kidneys.
- Cognitive Functions: Constant use may cause forgetfulness and decreased mental ability.
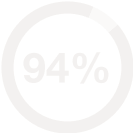
- Mental health: Increased likelihood of depression, anxiety, and other mental disorders.
Health Risks of Ketamine Use
| Health Risk | Percentage of Users Affected |
| Bladder damage | 25% |
| Kidney damage | 20% |
| Cognitive impairment | 30% |
| Mental health issues | 40% |
These statistics point out the critical need for awareness and precaution in using ketamine. Responsible use and an understanding of the potential health risks are the only means by which lifelong damage can be prevented.
Psychological and Cognitive Impacts
The implications of addiction to ketamine on a psychological and cognitive level are profound and pervasive. Prolonged use is often associated with severe memory impairments and an inability to concentrate on anything, thus impairing normal functioning. In addition, the effects of ketamine on changes in brain chemistry frequently exacerbate problems of depression and anxiety. Over time, these cognitive deficits and psychological challenges can significantly diminish the quality of life, underlining the urgent need for effective treatment and support for those struggling with ketamine addiction.
Social and Legal Consequences
Ketamine use can cause heavy social and legal implications. Socially, individuals often face strained relationships, job loss, and isolation due to their drug use. Legally, illicit use or distribution of ketamine can be seriously punished, either with hefty fines or imprisonment. The problems of ketamine addiction seep into all walks of life and point out the urgent necessity of comprehensive support and intervention measures.
Treatment Options for Ketamine Addiction
Treatment for ketamine addiction must, therefore, be multi-dimensional and integrated with the complicated nature of the dependency. Medical intervention includes detox programs to safely handle the withdrawal symptoms, followed by behavioral therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which focuses on the psychological part of the addiction. Support groups like Narcotics Anonymous offer a community for continuous support and accountability. Given how addictive ketamine is, combining medical intervention and CBT with some holistic approaches, such as mindfulness or even exercise, could further improve recovery in such a manner that offers a well-rounded path to overcoming addiction.
Detoxification Process
Detoxification is one of the very critical steps taken for ketamine addiction treatment. Basically, detoxification means the safe removal of drugs from the body and handling the effects of their withdrawal. The most critical components that assist during the detoxification process are:
- Symptom relief: Medications can be given to reduce anxiety, depression, and other withdrawal symptoms.
- Medical Supervision: It ensures that withdrawal symptoms are safely and effectively dealt with.
- Supportive care: Provision of correct nutrition, hydration, and rest to support the body's natural recovery process.
- Transition planning: This allows an individual to plan for further treatment and therapy necessary for dealing with the psychological aspect of ketamine addiction.
A structured detox program provides a foundation on which long-term recovery can be laid, and it prevents the occurrence of relapse.

Behavioral Therapies
Ketamine addiction treatment requires behavioral therapies to enable an addicted person to overcome the concealed factors behind one's dependency. Cognitive behavioral treatment has been proven to be very effective, as this therapy changes the negative thinking patterns and behaviors of a person that are linked with drug use. This kind of therapy enables people to adopt better ways of dealing with life's circumstances and avoiding relapse.
Another vital therapy, motivational interviewing, is also needed in ketamine therapy. This technique increases a person's motivation and commitment to change. This helps a person to have increased willpower for transcending addiction. These various therapies, when combined, prove to be an effective treatment plan that boosts long-term recovery chances for the patient.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can play a vital role in supporting individuals to move along the hurdles of defeating dependence on ketamine. While no medications are explicitly approved for ketamine addiction, some drugs may help decrease withdrawal symptoms and reduce the urge to use the drug. Examples include benzodiazepines (administered to lessen withdrawal anxiety and agitation during detox), and antidepressants (taken to counteract depression related to ketamine use). The combination of MAT with a more comprehensive addiction treatment plan will boost the likelihood of long-term recovery and stability.
Support Groups and Aftercare
Recovery from the abuse of ketamine requires support groups and aftercare as an integral part of treatment. Groups such as NA provide a sense of belonging and accountability by allowing members to share experiences with others who share similar problems. Aftercare programs provide continued access to support and resources, which help to thwart relapse and are conducive to long-term recovery. Such long-term support systems are essential in ensuring one maintains sobriety and faces all the negative consequences that ketamine abuse might have in store for the individual, giving one the necessary tools and support to live a drug-free life.
Overcoming the Hidden Dangers of Ketamine Addiction
It's essential to understand how addictive ketamine is and what health complications arise. While it proves beneficial from a medical perspective, it can have severe physical and mental health complications when used for recreation. Knowing the signs of abuse of ketamine and seeking comprehensive treatment options - including detoxification, behavioral therapies, and medication-assisted treatment - are vitally important steps in the recovery process. Support groups and aftercare programs help in maintaining long-term recovery from addiction. For those seeking professional help, the Canadian Centre for Addictions is an excellent choice for overcoming ketamine addiction and living a healthy, drug-free life.
FAQ
What is Ketamine?
Ketamine is a powerful anesthetic initially developed for medical use. Over time, it has also become popular for its mind-altering effects, leading to recreational use and potential addiction.
How is Ketamine used medically?
Besides being used as an anesthetic, ketamine is now employed off-label to treat severe depression. Administered in a controlled environment, it can quickly reduce depressive symptoms.
Why is Ketamine addictive?
Ketamine's euphoric and dissociative effects make it highly desirable. Regular use can lead to increased tolerance, physical dependence, and psychological addiction, especially when used recreationally.
What are the health risks of Ketamine misuse?
Misusing ketamine can cause serious health issues such as bladder and kidney damage, cognitive impairment, and mental health disorders like depression and anxiety.
How can Ketamine addiction be treated?
Treatment includes a combination of detoxification, behavioural therapies, medication-assisted treatment, support from groups and aftercare programs to ensure long-term recovery.